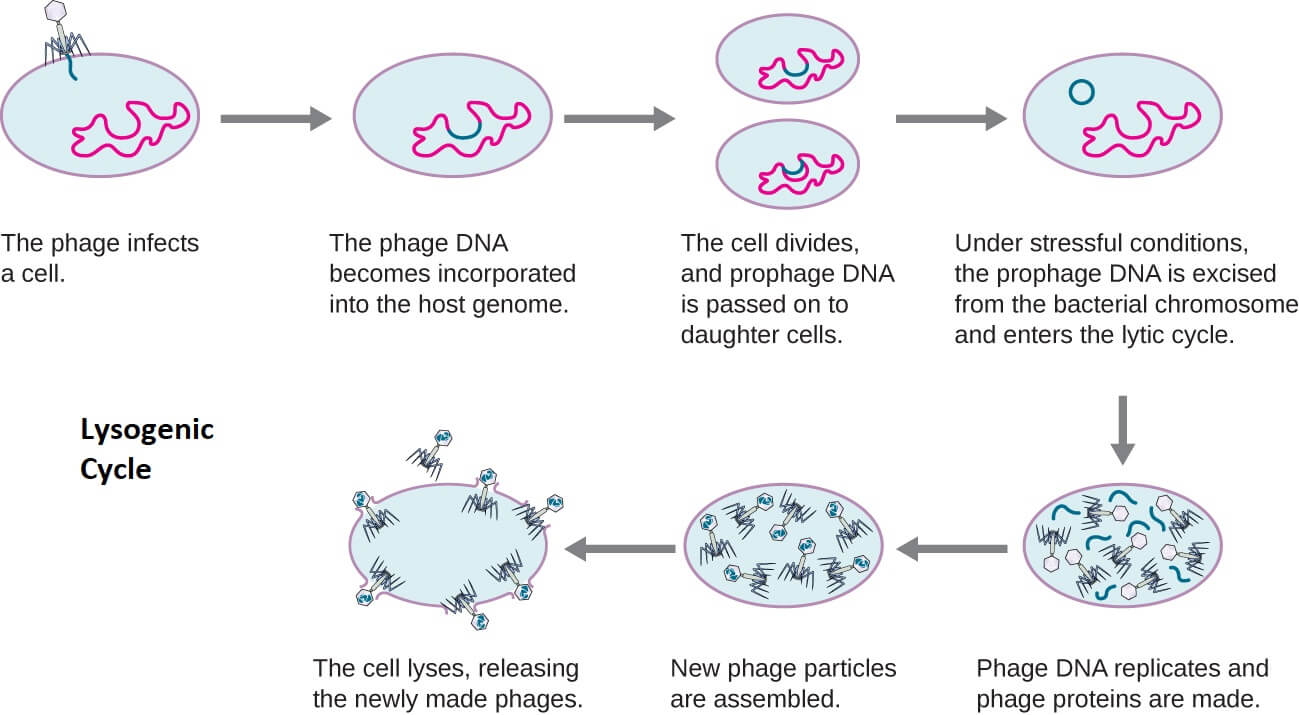
Describe the Lytic Cycle of T Even Bacteriophages
Five steps of Bacteriophage Lytic Cycle. Article shared by.
Bacteriophage Definition Structure Life Cycles Applications Phage Therapy
The lytic cycle also termed as vegetative life cycle or Infection cycle or sometimes Multiplication cycle results in the lysis rupture of the host cell.
. As a result a number of newly synthesized viral progeny is produced. Describe how bacteriophages are cultured. Unlike other DNA all the T-even phages contain 5-hydroxy-methyl-cytosin e instead of cytosine so that synthesis of phage can occur easily.
Simply mean bursting or rupturing cycle over and over again. Lysogenic cycle not a common method of viral reproduction majorly is dependant on the lytic cycle. Define a viral species and give an example of a family genus and common name of a virus.
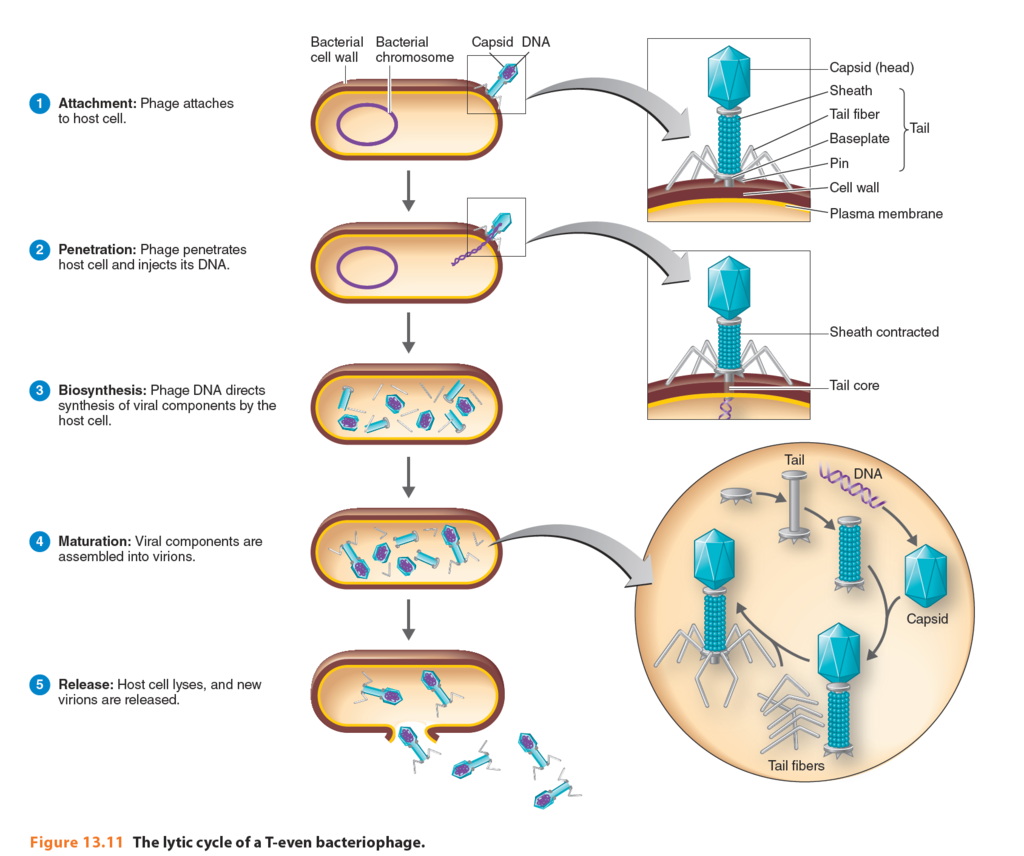
The multiplication processes of T-even phages are a little complex. This cycle takes place in the following steps. Phage tail fibers attach to specific receptors on bacteria.
Although similar at times understanding the difference between lytic cycle and. The bacterial cell is completely destroyed immediately after. Phage penetrates host cell and injects its DNA.
Lytic Cycle Virulent infection They induce complete lysis of the bacterial cell which is known as a lytic life cycle. Multiplication of T-Even Phages. The whole process involves following steps.
The average number of virons released by a cell 50-200 virons for T-even phage Adsorption Penetration Biosynthesis Maturation Release. This process is known as adsorption. After the lysis of host cells.
Two major cycles of multiplication of bacteriophages are. Examples include T2 T4 T6 T-even phages they are also known as virulent phages. Lytic Cycle or Virulent Cycle.
Describe the lysogenic cycle of bacteriophage lambda. It is accomplished in certain stages viz adsorption penetration synthesis replication maturation. In the Lytic Cycle a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release progeny virus.
The Life Cycle of Lambda Phages. Virulent or lytic cycle. T-even phage is a good example of a well-characterized class of virulent phages.
Lysogenic Cycle or Temperate Cycle. Lytic Cycle. Describe the lytic cycle of T-even bacteriophages Attachment - attachment or adsorption occurs between phage particles and bacteria.
Describe the lytic cycle of T-even bacteriophages. The lytic cycle is one of the two cycles of viral reproduction the other being the lysogenic cycle. Phage penetrates host cell and injects its DNA.
Induction à process by which phage reproduction is initiated in a. In this step the bacteriophage attaches itself by its tail to the cell wall of. There are five stages.
The phages undergoing lytic cycle are called lytic phages or virulent phages eg T-series bacteriophages. Phage attaches to host cell. The Lytic Cycle of T-even Bacteriophage T-Even Bacteriophages.
Figure 109 shows the lytic cycle of phage T4 and the main stages are described below. Phage DNA directs synthesis of viral components by the host cell. Figure 1311 The lytic cycle of a T -even bacteriophage.
Following are the steps of lytic cycle. Bacteriophages exhibit two types of replication cycle virulent or lytic cycle and temperate or lysogenic cycle Fig. This initial stage happens after a chance collision between a bacteria and phage particles.
The double-stranded linear DNA genome contains over 100 genes and is contained within the icosahedral head. This attachment is between two weak bonds that are formed at the receptor sites. Phage attaches to host cell.
During the lytic cycle of virulent phage the bacteriophage takes over the cell reproduces new phages and destroys the cell. Viral components are assembled into virions. It is circular and terminally redundant.
In this method the virus unites its genetic details with that of the host turning dormant and lets the host to reproduce while continuing its regular activities. Temperate phage à phage that is capeable of either setting up a lysogenic or lytic relationship with the host 4. The lytic cycle is typically considered the main method of viral replication since it results in the destruction of the infected cell and the release of new.
-Phage release enzyme - Lysozyme discovers part of the bacter. 1 Attachment bacteriophages contain fibers at the tail that attach to the complementary receptor on the host cell surface. In lytic cycle a lytic phage infects and kills the host cell to release progeny virions.
Principal events of viral infection in lytic cycle for bacteriophages. Lytic Cycle of T-Even Phages. Thus bacteriophages undergoing a lytic life cycle only are also known as virulent.
Host cell lyses and new visions are released. T-even Bacteriophage Lytic Cycle. Describe the principal events of attachment entry uncoating biosynthesis maturation and release of an enveloped DNA-containing virus.
The bacteriophage attaches itself on the surface of bacteria. The action of most of viral genes is to enable the viruses to infect their respective host cells multiply by using the host machinery such as enzymes and ribosomes and then causing the lysis of cells. Figure 108 A T-even bacteriophage.
Prophage à term used to describe a temperate phage that is being maintained with the host genome 5. Described how animal viruses are cultured. The virions fully developed viral particle of T-even bacteriophages are.
It is one of the cycles of a bacteriophage virus in which their is a master-slave relationship between the bacteriophage master and bacteria slave. The growth cycle is said to be lytic because it culminates in the lysis bursting of the host cell. Viral DNA takes over the machinery of the host cell and begins.
Phage DNA directs synthesis of viral components by the host cell.

Comments
Post a Comment